Hardware lifecycle management has evolved from a tactical procurement consideration to a strategic business imperative. Organizations that implement comprehensive hardware lifecycle strategies reduce total cost of ownership by 35-45%, minimize security vulnerabilities, and maintain competitive advantage. This guide examines proven frameworks for optimizing hardware from procurement through retirement. The Critical Importance of Strategic Hardware Lifecycle Management Modern enterprises face unprecedented challenges in managing hardware assets across distributed environments. Research from IDC reveals that organizations with immature lifecycle management practices experience: 42% higher total cost of ownership over 5 years 3.5× more security incidents due to outdated equipment 65% more unplanned downtime hours annually 28% lower employee productivity from aging hardware Comprehensive Hardware Lifecycle Management Framework Phase 1: Strategic Planning and Procurement Technology Assessment and Roadmapping Conduct thorough needs analysis across all business units Evaluate emerging technologies against organizational objectives Establish 3-5 year technology refresh cycles based on workload requirements Implement standardized hardware specifications across the organization Vendor Management and Sourcing Develop multi-vendor strategies to mitigate supply chain risks Negotiate lifecycle-based service level agreements (SLAs) Establish clear escalation paths and support structures Secure guaranteed product availability commitments Phase 2: Deployment and Integration Standardized Deployment Processes Implement automated provisioning and configuration management Establish comprehensive asset tracking and documentation Develop standardized imaging and deployment templates Create detailed network and integration specifications Performance Baselining Establish comprehensive performance metrics and monitoring Document initial configuration and performance characteristics Implement capacity planning and growth forecasting Set performance thresholds and alerting mechanisms Phase 3: Operational Management and Maintenance Proactive Maintenance Strategies Implement predictive maintenance using IoT sensors and analytics Establish regular firmware and security update schedules Conduct periodic performance and health assessments Maintain comprehensive service history and documentation Lifecycle Monitoring and Analytics Deploy automated asset management and monitoring systems Track hardware performance against established baselines Monitor warranty and service contract expiration dates Analyze utilization patterns and capacity requirements Phase 4: Refresh and Decommissioning Strategic Refresh Planning Develop data-driven refresh recommendations based on performance metrics Plan for technology migration and data transfer Coordinate hardware disposal with security and compliance requirements Implement green disposal and recycling practices Knowledge Transfer and Documentation Document lessons learned and best practices Update configuration management databases Transfer knowledge to operations and support teams Maintain comprehensive asset history for future planning Best Practices for Implementation 1. Establish Cross-Functional Governance Create a hardware lifecycle management committee with representatives from IT, finance, operations, and security. This team should: Define and enforce lifecycle policies Approve technology standards and exceptions Monitor compliance and performance metrics Manage budget and resource allocation 2. Implement Advanced Monitoring and Analytics Deploy comprehensive monitoring solutions that provide: Real-time hardware health and performance data Predictive failure analysis and alerting Utilization and capacity trending Automated reporting and dashboarding 3. Develop Comprehensive Documentation Maintain detailed records including: Hardware specifications and configurations Service histories and maintenance records Performance baselines and metrics Refresh schedules and replacement plans 4. Establish Clear Financial Planning Implement transparent budgeting processes that account for: Total cost of ownership calculations Refresh and replacement funding Maintenance and support costs End-of-life disposal expenses Measuring Success and ROI Organizations should track these key performance indicators: Financial Metrics Total cost of ownership reduction Return on investment for lifecycle management initiatives Budget variance for hardware refresh programs Cost avoidance through extended lifecycle management Operational Metrics Mean time between failures (MTBF) System availability and reliability Incident response and resolution times Asset utilization rates Strategic Metrics Technology refresh cycle compliance Security vulnerability reduction Employee satisfaction with hardware performance Business unit satisfaction with IT services Case Study: Global Financial Services Implementation A multinational bank implemented this comprehensive hardware lifecycle management framework and achieved: 42% reduction in total hardware costs over 3 years 99.95% infrastructure availability across 15,000 devices 67% decrease in security vulnerabilities from outdated equipment 35% improvement in IT staff productivity through standardized processes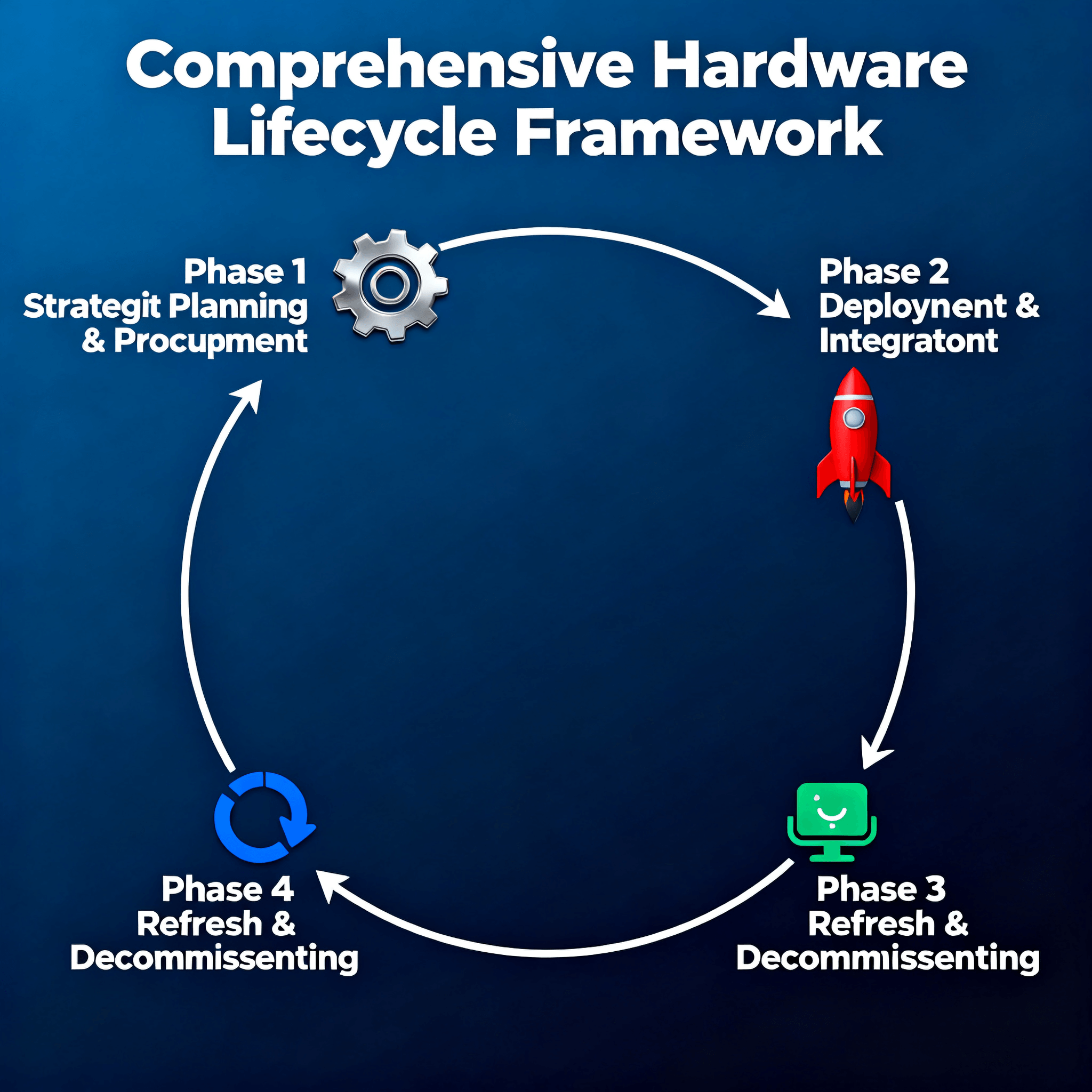
Contact: Tom
Phone: 86 18933248858
E-mail: tom@angxunmb.com
Whatsapp:86 18933248858
Add: Floor 301 401 501, Building 3, Huaguan Industrial Park,No.63, Zhangqi Road, Guixiang Community, Guanlan Street,Longhua District,Shenzhen,Guangdong,China
We chat
